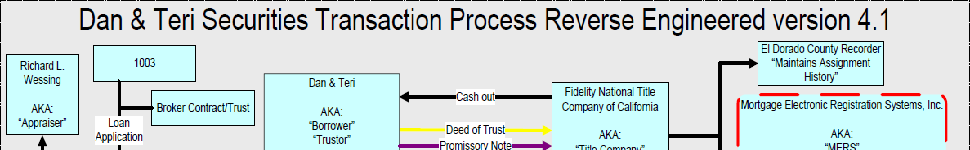
All Assignments of a Mortgage Must Be Recorded Before the Mortgagee Begins Foreclosure by Advertisement
All Assignments of a Mortgage Must Be Recorded Before the Mortgagee Begins Foreclosure by Advertisement
By Daniel Edstrom
DTC Systems, Inc.
The Minnesota Supreme Court issued a ruling requiring strict compliance with recording assignments prior to starting a foreclosure by advertisement.
Quote from the ruling:
Under Minn. Stat. § 580.02 (2012), all assignments of a mortgage must be recorded before the mortgagee begins the process of foreclosure by advertisement. Absent strict compliance with this requirement, a foreclosure by advertisement is void.
Affirmed.
Download the ruling here: http://dtc-systems.net/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Ruiz-vs-1st-Fidelity-Foreclosure-by-Advertisement-must-have-strict-compliance.pdf