The Wrong Remedy at the Wrong Time, Part 2
By Daniel Edstrom
DTC Systems, Inc.
New Note added on 1/22/2012 thanks to Simonee. California Probate Code does not seem to apply based on this California Supreme Court decision: Monterey S.P. Partnership v. W. L. Bangham, Inc. (1989) 49 Cal.3d 454 , 261 Cal.Rptr. 587; 777 P.2d 623 (download here: http://dtc-systems.net/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/Monterey_SP_Partnership_vs_WL_Bangham.pdf)
This is a continuation from The Wrong Remedy at the Wrong Time, Part 1 (http://dtc-systems.net/2011/01/wrong-remedy-wrong-time-part-1/).
 It turns out that if you want to modify the Trust created by your Deed of Trust, or if you want to determine if the trust exists, you need to petition the court under California Probate Code 17200. If you are not in California, but are in a Deed of Trust state, your state probably has similar probate laws.
It turns out that if you want to modify the Trust created by your Deed of Trust, or if you want to determine if the trust exists, you need to petition the court under California Probate Code 17200. If you are not in California, but are in a Deed of Trust state, your state probably has similar probate laws.
In order to petition the court, California Probate Code 17200 has the following provision:
“(a) Except as provided in Section 15800, a trustee or beneficiary of a trust may petition the court under this chapter concerning the internal affairs of the trust or to determine the existence of the trust.”
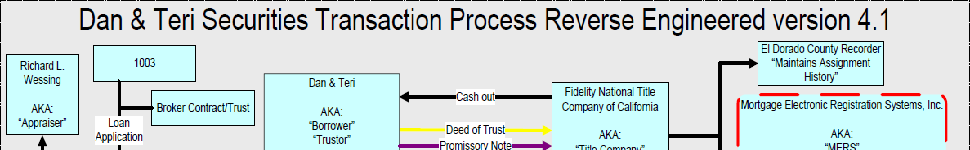
Right off the bat we find that only a trustee or a beneficiary has the ability to petition the court under 17200. If no trustee is specified, the default trustee is the trustor (the parties that executed the note – i.e. the homeowners). The beneficiaries can easily substitute in a new trustee if that occurs. But what if Mortgage Electronic Registration Systems (MERS) is named as the beneficiary? Consider California Mortgage and Deed of Trust Practice § 1.39 (3d ed Cal CEB 2008) § 1.39 (1) the Beneficiary Must Be Obligee: The beneficiary must be an obligee of the secured obligation (usually the payee of a note), because otherwise the deed of trust in its favor is meaningless. Watkins v Bryant (1891) 91 C 492, 27 P 775; Nagle v Macy (1858) 9 C 426. See §§ 1.8-1.19 on the need for an obligation. The deed of trust is merely an incident of the obligation and has no existence apart from it. Goodfellow v Goodfellow (1933) 219 C 548, 27 P2d 898; Adler v Sargent (1895) 109 C 42, 41 P 799; Turner v Gosden (1932) 121 CA 20, 8 P2d 505. The holder of the note, however, can enforce the deed of trust whether or not named as beneficiary or mortgagee. CC § 2936; see § 1.23.
Continue reading “The Wrong Remedy at the Wrong Time, Part 2”
 First, Nevada law is clear that “[a]n action for the tort of wrongful foreclosure will lie if the trustor or mortgagor can establish at the time the power of sale was exercised or the foreclosure occurred, no breach of condition or failure of performance existed on the mortgagor or trustor’s part which would have authorized the foreclosure or exercise of the power of sale.” Ernestburg v. Mortgage Investors Group, No. 2:08-cv-01304-RCJ-RJJ, 2009 WL 160241, at *6 (D. Nev. Jan. 22, 2009) (internal citations and quotations omitted). The plaintiff must establish that they were not “in default when the power of sale was exercised.” Id. (citing Collins v. Union Fed. Sav. & Loan Ass’n, 662 P.2d 610, 623 (Nev. 1983)). Furthermore, a claim for wrongful foreclosure does not arise until the power of sale is exercised. Collins, 662 P.2d at 623.
First, Nevada law is clear that “[a]n action for the tort of wrongful foreclosure will lie if the trustor or mortgagor can establish at the time the power of sale was exercised or the foreclosure occurred, no breach of condition or failure of performance existed on the mortgagor or trustor’s part which would have authorized the foreclosure or exercise of the power of sale.” Ernestburg v. Mortgage Investors Group, No. 2:08-cv-01304-RCJ-RJJ, 2009 WL 160241, at *6 (D. Nev. Jan. 22, 2009) (internal citations and quotations omitted). The plaintiff must establish that they were not “in default when the power of sale was exercised.” Id. (citing Collins v. Union Fed. Sav. & Loan Ass’n, 662 P.2d 610, 623 (Nev. 1983)). Furthermore, a claim for wrongful foreclosure does not arise until the power of sale is exercised. Collins, 662 P.2d at 623.