Irreconcilable Differences… I want a Mortgage Divorce!
By James Macklin
Secure Document Research
Promissory Note Terms Vs. PSA/Prosectus Terms
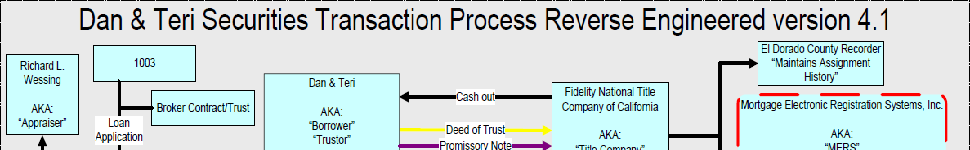
 When we are handed a voluminous stack of documents at the closing table for our mortgage transaction, a Borrower is expected to make a decision based upon the duty and care that the party who drafted these “investment contracts” has placed into them. However, none of us at the closing table has any idea what most of the words, phrases, and legal terminologies actually means… especially those affecting our rights as a consumer and as a real property owner.
When we are handed a voluminous stack of documents at the closing table for our mortgage transaction, a Borrower is expected to make a decision based upon the duty and care that the party who drafted these “investment contracts” has placed into them. However, none of us at the closing table has any idea what most of the words, phrases, and legal terminologies actually means… especially those affecting our rights as a consumer and as a real property owner.
Within the typical language of a Pooling and Servicing Agreement executed by the players of the securitization financing, there are countless references to the “interests” of the asset being conveyed, or, your Note and Deed. Interests are a finicky word of art used. The word simply means this: the asset, along with all of its’ benefits and liabilities. These are the “interests” being conveyed with the sale, set-over, transfer, conveyance, etc. So, under the terms of the Note we signed, look to the section titled: “Who is obligated under the Note” (usually sec. nine (9)). Here you will find that myriad entities may be, and probably are, also obligated under this same Note. These are the terms you have agreed to and bargained for. But the banking intermediaries would have us believe otherwise, as exhibited in the PSA under such language as: “The Depositor, Sponsor/Seller, Swap Counterparty, Master Servicer, Trustee do not intend for any obligation of themselves or their agents or employees to arise as a result of this Agreement”. This is contradictive to the terms and conditions that we have agreed to. Because the intervening assignments are a functional necessity to the bankruptcy remoteness of these assets, the specific substance of the PSA must be followed, including the mandate for the indorsement of each intervening assignment, along with the recordation of those assignment in the proper land title records office within the State of jurisdiction.
Let’s go back to the language of the “Who is Obligated” section of our Note. Notice that anyone who endorses the instrument is also obligated under the Note. Does this create an unknown Obligor at closing? If an un-named Beneficiary is the result of the unilateral agreement known as a Promissory Note”, how do we have the understanding necessary to execute such a critical document? It is the contention of this author, supported by the very agreements signed under oath and filed for record with the SEC, that “interests” and “obligations” are synonomous within the four corners of the agreement we signed…and the agreements signed by the intermediaries. A court of competent jurisdiction shall be posed these foundational questions very soon, and often. Are we a party to these agreements known as PSA/Prospectus? If we do a simple word search on each of these and look for references to: Borrower, Mortgagor, Obligor, we find these terms are typically used in excess of 60-75 times. Yet we were never disclosed the terms and conditions of the actual “loan” transaction as it truly was executed, and the rights, duties and responsibilities of the intermediaries. These are material disclosures relative to fees, expenses and various credit enhancements which are attributed to the Borrowers’ payment stream.
A divorce from this menagerie of deceit is not only appropriate, but a right that is being tried in many courtrooms. I believe that the judiciary will be tested on many platforms and small but visceral victories shall carry the day.