It isn’t clear why the American Securitization Forum decided to walk into a buzzsaw, but the carnage is proving to be an amusing spectacle.
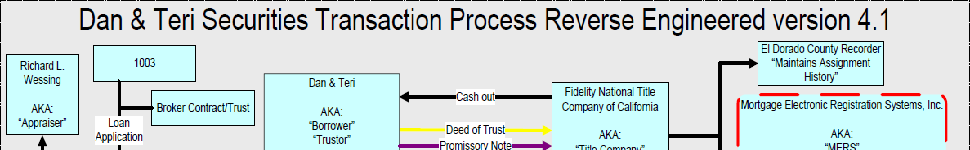
For readers who have not followed this wee saga, mortgage securitization abuses are increasingly looking to be a mess of Titanic proportions. The securitization industry created complex and specific procedures for getting the loans into the securitization legal vehicle, a trust. (The loan, meaning the borrower IOU, is called the note; confusingly, the lien is separate and called a mortgage or in some states, a deed of trust).
These procedures were complex for very good legal reasons. These securitizations had to pick their way very carefully through a thicket of issues: state-based real estate law; the Uniform Commercial Code; the desire to create bankruptcy remoteness (so if the originator went bust, the investors would not be exposed to the risk of lenders to the originator trying to get the notes back out of the trust); securities regulations; tax law; trust law.
These provisions were adhered to for nearly two decades. But sometime in the early 2000s, it appears that the industry simply quit observing the requirements of its own contracts, called pooling and servicing agreements. And the worst is that there are no simple fixes for the resulting mess.
If the breakdown was as widespread as it appears to be, at a minimum, in the overwhelming majority of states, it will become more and more difficult to foreclose as consumer lawyers and judges wise up to these issues. And in a worst case scenario, it is entirely possible in some, perhaps many cases, no assets got the the trusts by closing, which would make them void under New York law, which governs virtually all mortgage securitization trusts (even if true, investors may choose not to pursue that theory in a lawsuit, but more evidence of pervasive problems may lead investors use related theories to press to have the deal unwound, which is still a pretty dire outcome).
The American Securitization Forum which represents originators (it also has investors as members, but investors and independent observers see the ASF as very much originator-oriented) has decided to come out guns-a-blazing against critics. The problem is, however, that it has neither the law or facts on its side. Its strident attacks are looking a wee bit desperate.
In recent Congressional hearings, the ASF executive director Tom Deutsch provided testimony that was truly astonishing (see here and here). It asserted, in effect, that extremely clear and easy to interpret language in the PSA about how the notes were to be conveyed to the securitization meant the opposite of what they said. The contracts call for a “complete” or “unbroken” chain of endorsements. The ASF testimony argued that that very same language meant the very opposite, that no such thing needed to happen. And the testimony peculiarly personalized the attack, fixating on Georgetown law professor Adam Levitin. Even though he has almost become a fixture on Congressional panels on this topic, he is far from the only expert to have argued for this interpretation.
Levitin deigned to address the ASF argument, and his post, “Fisking the American Securitization Forum’s Congressional Testimony,” is engaging. I suggest you read it in its entirely. Here are some of the key bits:
My first thought was “gosh, ASF’s awfully defensive. They sure seem spooked.” And on looking at the details of the ASF’s rebuttal, my sense is they’re on very shaky ground if these are the best arguments they have….
ASF takes me to task because the argument I make about PSAs is not supported by caselaw. Duh. Of course it isn’t. These issues have never been litigated. The whole point I’ve been making is that there are a bunch of unresolved legal issues. I’m not the one who decides what the outcome is. I can only offer my semi-learned opinion. But just as my argument lacks caselaw support, so too does that of the ASF. At least I’m not the one who built a $1.2 trillion dollar private label residential mortgage securitization industry hinging on uncertain law…..
ASF argues that the language in many PSAs requiring a “complete” or “unbroken” chain of endorsements only means that there must be a chain of endorsements legally sufficient to effectuate the transfer of the note to the trust…
There are a few problems with this argument. First, if the ASF is correct in its claim that the loans are transferred by sale under Article 9 of the UCC, the legal sufficiency of the endorsements should simply be irrelevant. In making this claim, ASF seems to be conceding that PSAs are the governing law for RMBS transactions.
Second, it’s worth looking at the entire language used in PSAs, not the selectively quoted language referred to by the ASF. For example, consider the PSA for Securities Asset Backed Receivables LLC Trust 2005-FR3, dated July 1, 2005, § 2.01(b), July 1, 2005. It provides that the depositor will deliver to the trust:
“the original Mortgage Note bearing all intervening endorsements showing a complete chain of endorsement from the originator to the last endorsee, endorsed ‘Pay to the order of _____________, without recourse’ and signed (which may be by facsimile signature) in the name of the last endorsee by an authorized officer.”
Note the bold language (my emphasis; the italics are original). There can be no question that this language is calling for every endorsement from the originator to the trust, and cannot be satisfied with a single endorsement in blank. For deals with this language, at least, ASF’s testimony is demonstrably wrong.
Now, it is important to note that not every PSA has such language…The incidence of various PSA language is unknown, but certainly there are a good number of PSAs where there has to be a complete chain of endorsements.
Another inconvenient fact is, contrary to the ASF assertions, that judges are also looking for the chain of endorsements to make sense, without reference to the PSA. By happenstance, April Charney sent a Florida decision today which illustrates how the lack of proper endorsements derailed a foreclosure (April has graciously included me in her frequent updates to various groups of lawyers involved in foreclosure defense).
Order for BAC Home Loans Servicing v. Stentz
This order is short and make for instructive reading. The note in question was indorsed (bankruptcy courts use “indorse” for “endorse”) in blank, something the ASF says is perfectly kosher. The Florida judge is not entirely comfortable with that, noting that Florida law requires that the party prosecuting a foreclosure both own and be the holder of the note. He dismissed the case without prejudice, but notice the requirements he stipulates for any amended complaint (boldface mine):
1. Allege additional facts, not conclusions of law, that specifically set forth the and identify the present owner of the note and mortgage and the present holder of the note and mortgage and in so doing deraign the chain of ownership/holdership since the loan’s inception.
2. Allege additional facts why the note is indorsed in blank and specifically deny, if that be the case, that it or an interest has been pledged to another….
5. Allege and identify all documents, by attachment, upon which Plaintiff relies to establish ownership of the note and mortgage.
Now look at the mess we have here. How, pray tell, are the plaintiffs going to prove how the note traveled from originator to its purported current owner in the absence of having the note endorsed with a full and unbroken chain of assignments? How are they going to prove a negative (as in 2, that it wasn’t pledged to another party? How will the plaintiffs prove the transfers? A basic feature of negotiable instruments like mortgage notes is that they are transferred by delivery, not by contract or assignment, AND that the party making the transfer must endorse the instrument so that it is payable to the recipient (or it can be endorsed in blank).
Oh, and if the borrower’s attorney is at all savvy, he will find the PSA for this loan. If the plaintiffs try to claim the conveyance chain was different than that stipulated in the PSA (something the ASF also tried to argue was fine), and the borrower’s counsel points out the discrepancy. This judge looks to be the sort that would find it troubling.
Here, again by virtue of synchronicity via April Charney yesterday, is another example of a judge, this time in Ohio, refusing to foreclose. One of the reasons is the chain of assignments is broken (see the part I boldfaced):
Case: CV-09-706959
Case Caption: PROVIDENT FUNDING ASSOCIATES, L.P. vs. TAMARA TURNER, ET AL
Judge: TIMOTHY MCCORMICK
Room: 20C JUSTICE CENTER
Docket Date: 11/09/2010
Notice Type: (JEPC) JOURNAL ENTRY NOTICE
Notice ID/Batch: 16552802 – 875214
To: JAMES R DOUGLASS
MOTION OF THE DEFENDANTS PHILLIP TURNER AND TAMARA TURNER TO DISMISS FOR PLAINTIFF’S LACK OF STANDING TO FILE THE FORECLOSURE IS GRANTED. PLAINTIFF DID NOT PRESENT EVIDENCE TO THE COURT THAT IT OWNED THE SUBJECT PROMISSORY NOTE AS OF THE DATE OF THE FILING OF ITS COMPLAINT IN THIS CASE AND COULD NOT, THEREFORE, PROVE THAT IT HAD STANDING TO FILE THIS CASE. SEE WELLS FARGO BANK V. JORDAN, 2009 OHIO 1092 (8TH DIST. CT. APP., MAR. 12, 2009). MERS COULD NOT ASSIGN THE NOTE AS IT NEVER HELD THE PROMISSORY NOTE. THERE IS NO EVIDENCE THAT THE ALLONGE WAS EVER AFFIXED TO THE NOTE. VIRTUAL BANK PURPORTS TO INDORSE THE NOTE TO THE PLAINTIFF, BUT THERE IS NO EVIDENCE THAT VIRTUAL BANK HELD THE NOTE AT THE TIME OF THE INDORSEMENT. VIRTUAL BANK IS ALSO NOT THE PAYEE ON THE NOTE. COMPLAINT DISMISSED WITHOUT PREJUDICE. AS PLAINTIFF DID NOT HAVE STANDING TO FILE THIS CASE, THE COUNTERCLAIM IS ALSO DISMISSED WITHOUT PREJUDICE. (FINAL)
COURT COST ASSESSED TO THE PLAINTIFF(S).
CLDLJ 11/09/2010
NOTICE ISSUED
Ohio and Florida require that the party foreclosing be the owner of the note. But even in states like California, which appear merely to require that the foreclosing party be a holder, “holder” signifies more than mere possession. In IndyMac Federal v. Hwang, the judge cites the California Commercial Code (3301 (a) and 1201 (20)) and UCC (3-301 (a) and 1-201 (20)):
For an instrument payable to an identified person (such as a note in this case), there are two requirements for a person to qualify as a holder: (a), the person must be in possession of the instrument and (b) the instrument must be payable to that person.
These examples prove a basic point. There is good reason why the PSAs stipulated a complete, unbroken chain of endorsements. The absence of them creates huge problems, independent of the requirements of the PSA, in enforcing the note.
As we said in our New York Times op-ed,
The people who so carefully designed the mortgage securitization process unwittingly devised a costly trap for people who ran roughshod over their handiwork. The trap has closed — and unless the mortgage finance industry agrees to a sensible way out of it, the entire economy will be the victim.
The ASF, perversely or perhaps predictably, is persisting in being part of the problem rather than part of the solution.
Read more on Trust, Securitization at Wikinvest
 loan is liquidated. It is also of value to note that usually the principal and interest is advanced until the loan is liquidated (as I saw in a case where it was stated by Deutsche Bank National Trust Company in an answer to discovery). So principal and interest payments are made by the servicers and/or trustees, and no loss is actually realized until after the house is foreclosed upon and sold to a 3rd party. So what came first, the default or the loss? No default occurs until the loan is liquidated, which doesn’t occur until after the foreclosure sale. This means the homes are sold while the loans are current. I would venture to say that nearly ALL foreclosures in at least the last 10 years on homes with securitized transactions, have been fraudulent and invalid. This is because the paperwork used to foreclose is VOID. Not voidable, but VOID.
loan is liquidated. It is also of value to note that usually the principal and interest is advanced until the loan is liquidated (as I saw in a case where it was stated by Deutsche Bank National Trust Company in an answer to discovery). So principal and interest payments are made by the servicers and/or trustees, and no loss is actually realized until after the house is foreclosed upon and sold to a 3rd party. So what came first, the default or the loss? No default occurs until the loan is liquidated, which doesn’t occur until after the foreclosure sale. This means the homes are sold while the loans are current. I would venture to say that nearly ALL foreclosures in at least the last 10 years on homes with securitized transactions, have been fraudulent and invalid. This is because the paperwork used to foreclose is VOID. Not voidable, but VOID.